ADDTECH | Ebike Mechanical Components - Brakes
By Addmotor | 27 March 2024 | 0 Comments
Electric bikes, with their higher speeds and increased weight compared to traditional bicycles, require reliable brakes to ensure optimum stopping performance and control while riding. Effective brakes not only help you maintain control but also keep them out of harm's way on the road, preventing potentially dangerous situations.
Therefore, the brake’s performance should be one of your top priorities when getting a new electric bike.
This article gives you a better understanding of ebike brake systems, helping you make an informed decision to find the brake system that best suits your needs.

Electric bikes often travel at higher average speeds than traditional bikes, except road bikes. Additionally, they can accelerate quickly, resulting in more frequent braking, especially in urban environments.
The combination of higher weights and speeds demands more strong and responsive brakes to overcome the momentum and ensure a safe stopping distance.
There are two main e-bike braking methods that can meet all these demands: rim brakes and disc brakes.
1. Rim Brakes: These brakes use friction to slow the bike down by pressing brake pads against the rims of the wheels. There are two sub-types:
Therefore, disc brakes have become the preferred choice for most e-bike companies like Addmotor, offering reliable and consistent braking performance and efficiency.
That’s why, in this guide, we will focus on the categories of Disc Brakes, which are mechanical brakes and hydraulic brakes. However, for now, let's leave it for discussion in the next section.
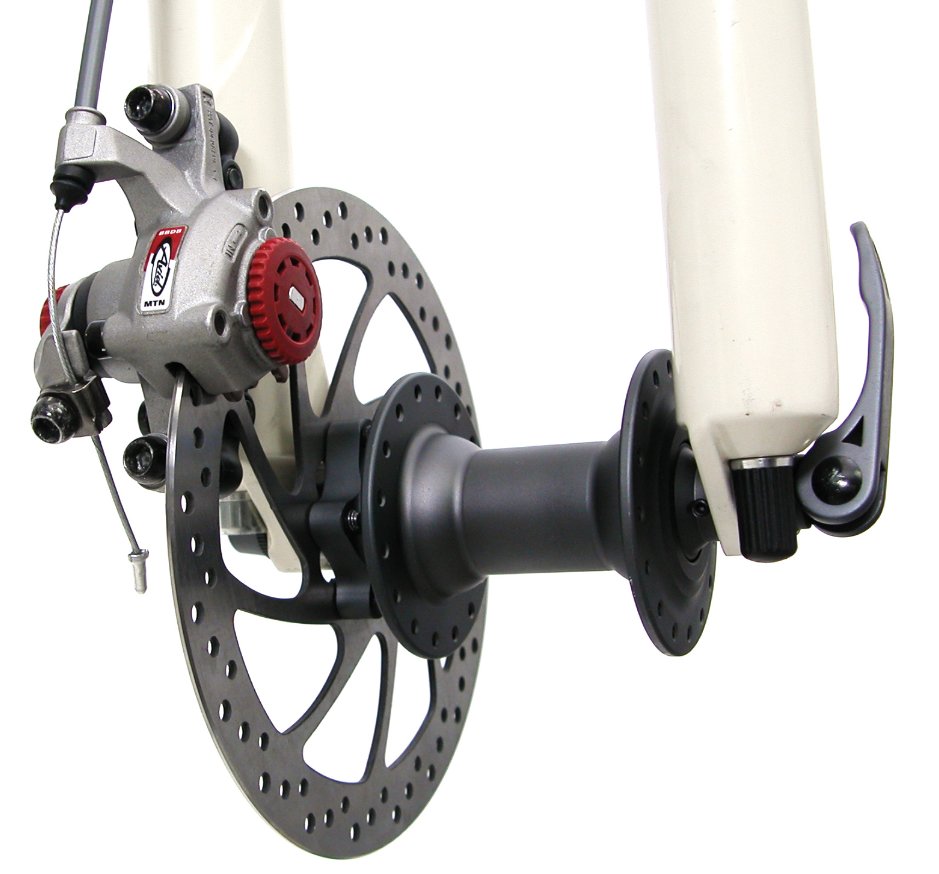

https://www.parktool.com/en-us/blog/repair-help/avid-mechanical-disc-adjustment
Mechanical disc brakes, also known as cable disc brakes. These brakes feature a straightforward setup consisting of a cable, brake lever, and a mechanical disc.
It uses a steel cable-actuated mechanism to engage the brake caliper when the brake lever is pulled. This action brings the brake pads into contact with the rotor on the wheel, effectively slowing down or stopping the e-bike. While they may not match the performance level of hydraulic brakes, they still offer reliable stopping power and modulation.
The Addmotor ARISETAN II M-360 and Grandtan II M-340 eTrikes feature robust 180mm Mechanical Disc Brakes, ensuring ample stopping power even in challenging conditions.
Advantages of Mechanical Disc Brakes: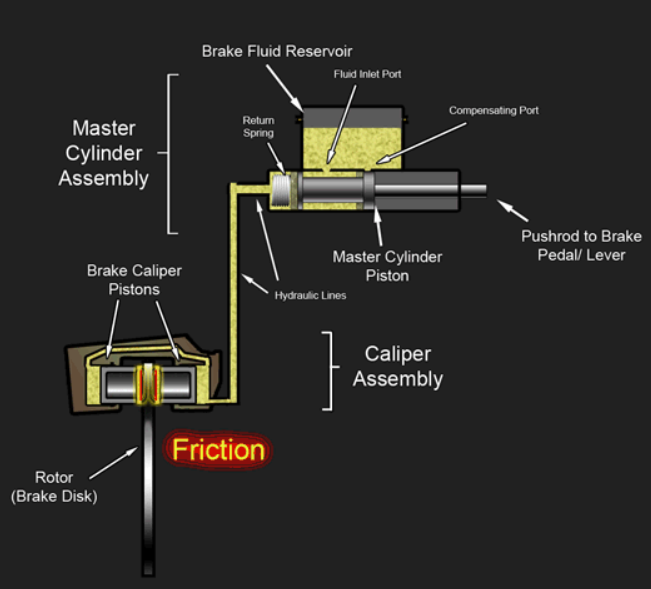
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydraulic_brake
Hydraulic disc brakes stand out as the top choice for e-bikes, renowned for their exceptional performance and reliability. They are operating through a sealed fluid system designed to transmit braking force from the lever to the caliper.
Within this hydraulic braking mechanism, a piston, and master cylinder hold brake fluid. When the rider squeezes the brake lever, the piston inside the cylinder moves, propelling brake fluid toward the brake caliper.
This force is subsequently transmitted to pistons within the brake caliper, compelling the brake pads to make contact with the disc rotor. As a result, the rotation of the rotor and wheel is slowed down, facilitating effective braking.
Models such as the CITYPRO E-43, CITYPRO E-53, and the GAROOTAN M-81 exemplify this system, utilizing fluid dynamics to deliver unparalleled stopping power and modulation.
Advantages of Hydraulic Disc Brakes:
Hydraulic systems leverage hydraulic pressure to power the pistons, while mechanical systems rely on friction between a pad and a rotating drum connected to one or two calipers.
Conversely, hydraulic disc brakes offer superior control and precision over braking force due to the minimal effort required to apply the brake. Squeezing the lever gently allows for precise modulation of braking force, reducing the likelihood of wheel lock-up and providing a smoother braking experience.
In contrast, hydraulic disc brakes tend to produce better-stopping power than mechanical brakes due to their increased efficiency. Hydraulic systems multiply the force applied to the lever, creating more braking power than input into the system. Additionally, hydraulic systems produce minimal friction, resulting in less energy loss within the system.
On the other hand, mechanical brakes may experience friction and resistance in the cable system, resulting in a less smooth and consistent braking experience. However, with proper maintenance and setup, mechanical disc brakes can still provide smooth operation and consistent braking force.
Hydraulic disc brakes are more expensive to purchase and maintain, and spare parts may be harder to come by, especially in remote regions where access to high-end bike shops is limited.
To understand better how these brakes differ, we compared two models from Addmotor, the Grandtan II M-340, which has mechanical brakes, and the GAROOTAN M-81, which comes with hydraulic brakes.
In contrast, mechanical disc brakes may experience reduced performance in wet weather due to cable stretch and friction.
Therefore, the brake’s performance should be one of your top priorities when getting a new electric bike.
This article gives you a better understanding of ebike brake systems, helping you make an informed decision to find the brake system that best suits your needs.

Ebike Braking System: Breaking Down the Basics
Ebike brakes function quite similarly to traditional bicycle brakes but must handle the additional weight of an e-bike's reinforced frames, battery, motor, and other electrical components.Electric bikes often travel at higher average speeds than traditional bikes, except road bikes. Additionally, they can accelerate quickly, resulting in more frequent braking, especially in urban environments.
The combination of higher weights and speeds demands more strong and responsive brakes to overcome the momentum and ensure a safe stopping distance.
There are two main e-bike braking methods that can meet all these demands: rim brakes and disc brakes.
1. Rim Brakes: These brakes use friction to slow the bike down by pressing brake pads against the rims of the wheels. There are two sub-types:
♦ Caliper brakes: Typically found on road bikes, these brakes are lighter but may be less powerful.
♦ V-brakes: More powerful, these brakes are commonly found on mountain bikes.
♦ V-brakes: More powerful, these brakes are commonly found on mountain bikes.
2. Disc Brakes: These brakes utilize a rotor and brake pads to slow down the bike. They are generally more powerful than rim brakes and offer superior stopping power and consistency. Its sub-types are:
♦ Mechanical disc brakes: They use a cable to activate the brake.
♦ Hydraulic disc brakes: These brakes use fluid to activate the brake, providing smoother and more precise braking.
♦ Hydraulic disc brakes: These brakes use fluid to activate the brake, providing smoother and more precise braking.
But, which brakes for E-Bikes are the best?
Between these two, disc brakes offer superior braking power compared to rim brakes due to their design, which places the braking surface closer to the brake pads. This proximity increases leverage, allowing disc brakes to apply more force to the wheel, resulting in stronger braking performance. Additionally, disc brakes maintain consistent effectiveness even in wet conditions, unlike rim brakes.Therefore, disc brakes have become the preferred choice for most e-bike companies like Addmotor, offering reliable and consistent braking performance and efficiency.
That’s why, in this guide, we will focus on the categories of Disc Brakes, which are mechanical brakes and hydraulic brakes. However, for now, let's leave it for discussion in the next section.
Components of an Electric Bike Brake System
A typical e-bike brake system consists of several key components:1. Brake Levers: These are used by the rider to activate the brake system. When the lever is squeezed, it either pulls on a cable or activates a hydraulic system, applying pressure to the brake pads.
2. Brake Pads: These are the components of the brake system that make contact with the wheel rim or disc rotor to slow down or stop the bike.
3. Motor Cutoff Switch: This safety feature is unique to electric bikes, which also known as the brake cutoff switch, is a mechanical or magnetic switch integrated into the braking system. When the brake lever is pulled, it sends a signal to the motor controller to turn off the motor, ensuring that the motor and brakes cannot be used simultaneously for safety reasons.
4. Calipers: Calipers hold the brake pads in place and apply pressure to them when the brake lever is squeezed. They can be either mechanical or hydraulic, depending on the brake system.
5. Brake Cables: In a mechanical brake system, the brake levers are connected to the calipers by cables. When the lever is squeezed, it pulls on the cable, applying pressure to the brake pads.
6. Brake Rotors: In a disc brake system, the brake pads squeeze a rotor mounted to the wheel hub to slow down or stop the bike. Rotors can be made of materials such as steel or aluminum.
7. Pistons: Pistons are present inside the master cylinder of hydraulic brake systems. The number of pistons varies between brake systems, with more pistons typically resulting in greater stopping power. When the piston moves, it compresses fluid or air inside the master cylinder, transferring brake force from the lever to the rotor.
Mechanical and Hydraulic Disc Brakes: Understanding the Technology
Mechanical Brakes

Mechanical disc brakes, also known as cable disc brakes. These brakes feature a straightforward setup consisting of a cable, brake lever, and a mechanical disc.
It uses a steel cable-actuated mechanism to engage the brake caliper when the brake lever is pulled. This action brings the brake pads into contact with the rotor on the wheel, effectively slowing down or stopping the e-bike. While they may not match the performance level of hydraulic brakes, they still offer reliable stopping power and modulation.
The Addmotor ARISETAN II M-360 and Grandtan II M-340 eTrikes feature robust 180mm Mechanical Disc Brakes, ensuring ample stopping power even in challenging conditions.
Advantages of Mechanical Disc Brakes:
♦ Easy to replace
♦ Cost-effective
♦ Simple maintenance
Disadvantages of Mechanical Disc Brakes:
♦ Requires more hand pressure to activate
♦ Needs frequent maintenance
♦ The brake cable may stretch
♦ Heavier
Hydraulic Brakes

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydraulic_brake
Hydraulic disc brakes stand out as the top choice for e-bikes, renowned for their exceptional performance and reliability. They are operating through a sealed fluid system designed to transmit braking force from the lever to the caliper.
Within this hydraulic braking mechanism, a piston, and master cylinder hold brake fluid. When the rider squeezes the brake lever, the piston inside the cylinder moves, propelling brake fluid toward the brake caliper.
This force is subsequently transmitted to pistons within the brake caliper, compelling the brake pads to make contact with the disc rotor. As a result, the rotation of the rotor and wheel is slowed down, facilitating effective braking.
Models such as the CITYPRO E-43, CITYPRO E-53, and the GAROOTAN M-81 exemplify this system, utilizing fluid dynamics to deliver unparalleled stopping power and modulation.
Advantages of Hydraulic Disc Brakes:
♦ Increased stopping power
♦ Longer lifespan
♦ Better modulation
♦ Superior heat dissipation
♦ Greater braking power
Disadvantages of Hydraulic Disc Brakes:
♦ Complex maintenance procedures
♦ Higher cost
♦ Difficult to fix if there's an oil leak
Comparative Analysis of Hydraulic Vs. Mechanical Brakes
1. Operating Principles:
Mechanical disc brakes utilize a cable system to engage the brake pads and activate the brakes. In contrast, hydraulic disc brakes rely on the use of pressurized braking fluid to compress the caliper's pistons and apply force to the rotor, effectively reducing its speed.Hydraulic systems leverage hydraulic pressure to power the pistons, while mechanical systems rely on friction between a pad and a rotating drum connected to one or two calipers.
2. Control and Precision of Braking Force:
Mechanical disc brakes require more pulling force on the brake lever, making it harder to control the braking force accurately and potentially leading to inefficiency in stopping power.Conversely, hydraulic disc brakes offer superior control and precision over braking force due to the minimal effort required to apply the brake. Squeezing the lever gently allows for precise modulation of braking force, reducing the likelihood of wheel lock-up and providing a smoother braking experience.
3. Stopping Power:
Mechanical brakes experience energy loss due to friction in the cable, potentially reducing the effectiveness of stopping power and resulting in longer stopping distances.In contrast, hydraulic disc brakes tend to produce better-stopping power than mechanical brakes due to their increased efficiency. Hydraulic systems multiply the force applied to the lever, creating more braking power than input into the system. Additionally, hydraulic systems produce minimal friction, resulting in less energy loss within the system.
4. Operation Smoothness and Braking Consistency:
Hydraulic disc brakes offer smoother and more consistent operation compared to mechanical brakes. The closed hydraulic system ensures smooth lever action without the risk of contamination by dirt or debris, leading to predictable and consistent braking force.On the other hand, mechanical brakes may experience friction and resistance in the cable system, resulting in a less smooth and consistent braking experience. However, with proper maintenance and setup, mechanical disc brakes can still provide smooth operation and consistent braking force.
5. Pricing and Parts Availability:
Mechanical disc brakes are generally more affordable than hydraulic brakes and have lower maintenance costs. Additionally, spare parts for mechanical brakes, such as levers and cables, are widely available in bike shops.Hydraulic disc brakes are more expensive to purchase and maintain, and spare parts may be harder to come by, especially in remote regions where access to high-end bike shops is limited.
To understand better how these brakes differ, we compared two models from Addmotor, the Grandtan II M-340, which has mechanical brakes, and the GAROOTAN M-81, which comes with hydraulic brakes.
| Categories | Grandtan II M-340(Mechanical brake) | GAROOTAN M-81 (Hydraulic brake) |
| Operation | Offers adequate stopping power | More efficient due to lack of cable friction |
| Sealed System | Easy to set up and maintain, with readily available replacement parts. | Its sealed system prevents dirt and mud buildup, requiring less maintenance over time. |
| Riding Needs | Provides adequate braking power for gravel riding and adventure cycling, offering reliability and simplicity for off-road exploration. | Offers superior modulation and control, making them ideal for technical off-road riding and high-performance applications. |
| Ease of Modulation | Allows for precise control over braking force | Provides better modulation and control over the braking force |
| Replacement | Components are easier and cheaper to replace. | More likely to last longer with less maintenance. |
| Repair Process | Easier repair process | Enclosed design to reduce maintenance frequency |
Factors Influencing Brake System Choice
Riding Conditions:
1. Urban Commuting: For city riding, where frequent stops and starts are common, riders may prefer hydraulic disc brakes for their superior stopping power and responsiveness.
2. Off-Road Trails: When navigating challenging terrain, such as gravel paths or rocky trails, hydraulic disc brakes excel due to their precise modulation and consistent performance.
3. Long-Distance Touring: For extended rides where reliability and durability are paramount, mechanical disc brakes may be preferred for their simplicity and ease of maintenance.
Weather Conditions:
Hydraulic disc brakes tend to perform better in wet conditions, as their sealed system prevents water ingress and maintains consistent braking power.In contrast, mechanical disc brakes may experience reduced performance in wet weather due to cable stretch and friction.
Riding Styles:
1. Casual Riding: If you seek comfort and ease of use, you can opt for mechanical disc brakes, which provide adequate stopping power for leisurely rides and are simpler to maintain.
2. Mountain Biking: For technical trails and aggressive riding, hydraulic disc brakes offer superior control and modulation, allowing riders to navigate steep descents and tight corners with confidence.
3. High-Speed Commuting: Commuters who prioritize safety and responsiveness may prefer hydraulic disc brakes for their quick and precise stopping ability, especially in heavy traffic or emergencies.
Conclusion
Each type of brake system, whether hydraulic or mechanical, has its own unique features and benefits that cater to different preferences and requirements. Ultimately, the choice depends on the individual cyclist.
When considering whether to opt for hydraulic or mechanical brakes, factors such as budget, riding conditions, maintenance needs, and personal preferences should be carefully considered. It's crucial to choose a braking system that prioritizes safety while providing an enjoyable riding experience.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.Required fields are marked. *
Latest Stories

_1713256451.jpg)


